基本介绍
- 分而治之(divide-andconquer):
- 自根至叶的递归过程
- 在每个中间结点寻找一个”划分”属性
- 过程:
- 把数据集分成两组
- 不同数据点被完美区分(Pure)开了么?
- 不是:重复楼上两步
- 是的:打完收⼯
建树逻辑
所有子树信息价值(信息熵、基尼指数等)的和必定小于等于原来整体数据集的信息价值,信息增益用来衡量减少的程度
def build(D=数据集):
if D所有数据目标值 y 都相同:
return #递回停止条件
for i in D中的所有特征:
计算用i划分子树后获得的信息增益
if 所有特征都没有大于零的信息增益:
return #递回停止条件
被选择的特征 x = 具有最大信息增益的特征
for sub in 按照x划分子树后的数据集:
build(sub)
停止条件
- 当前结点包含的样本全属于同一类别,无须划分
- 当前属性集为空,或是所有样本在所有属性上取值相同,无法划分
- 当前结点包含的样本集合为空,不能划分
特性
- 优势:
- ⾮⿊盒
- 轻松去除⽆关attribute (Gain = 0)
- Test起来很快 (O(depth))
- 劣势:
- 只能线性分割数据
- 贪婪算法 (每次分裂都选最好,有可能不是全局最好)
信息价值指标
信息熵
信息熵是度量样本集合”纯度”最常用的一种指标,假定当前样本集合D中第i类样本所占的比例为$P_i$,则D的信息熵定义为:
- 某随机事件结果的种类越多,则该事件的熵越大(不确定性越大)
- 某随机事件的各种可能发生结果概率越均匀,则该事件的熵越大(不确定性越大)
- 值域:>= 0
- 缺点是计算量大(log)
信息增益(ID3)
信息增益率(C4.5)
基尼指数(CART)
常见算法
- ID3:
- 只能使用熵的信息增益处理离散特征的分类问题
- 取值高的属性,更容易使数据更纯,其信息增益更大
- 训练得到的是一棵庞大且深度浅的树(可以把N个数据分成100%纯洁的N组)
- C4.5:
- 支持连续特征,在计算信息增益比之前首先将其离散化(与ID3差别)
- 使用信息增益比的概念去除先选择多值特征的倾向
- 在训练后检测训练集的正确分类比,并剪枝产生错误较多的叶子结点
- CART算法:
- 使用基尼系数代替熵进行信息增益计算、只使用二叉树,并提供解决回归问题的能力
- 以最小化不纯度,而不是最大化信息增益
DecisionTreeClassifier
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
iris = datasets.load_iris()
iris_data = iris['data']
iris_label = iris['target']
iris_target_name = iris['target_names']
X = np.array(iris_data)
Y = np.array(iris_label)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.25)
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier()
clf = clf.fit(x_train, y_train)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc
y_pred = clf.predict(x_test)
false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate, thresholds = roc_curve(
y_test, y_pred, pos_label=2)
roc_auc = auc(false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate)
roc_auc
|
1.0
调参
超参数:
- criterion: gini, entropy
- max_depth
- min_samples_split
- min_samples_leaf
- max_features
- max_leaf_nodes
- min_impurity_decrease
max_depth
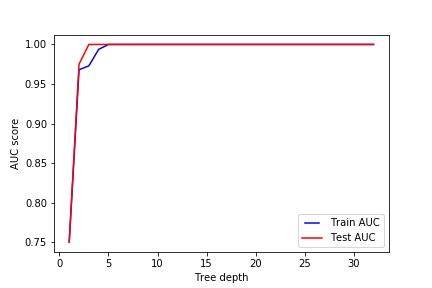
要调整的第一个参数是max_depth(树的深度)。 树越深,它就分裂的越多,更能捕获有关数据的信息。 我们拟合一个深度范围从1到32的决策树,并绘制训练和测试auc分数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| from matplotlib.legend_handler import HandlerLine2D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
max_depths = np.linspace(1, 32, 32, endpoint=True)
train_results = []
test_results = []
for max_depth in max_depths:
dt = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=max_depth)
dt.fit(x_train, y_train)
train_pred = dt.predict(x_train)
false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate, thresholds = roc_curve(
y_train, train_pred, pos_label=2)
roc_auc = auc(false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate)
train_results.append(roc_auc)
y_pred = dt.predict(x_test)
false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate, thresholds = roc_curve(
y_test, y_pred, pos_label=2)
roc_auc = auc(false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate)
test_results.append(roc_auc)
line1, = plt.plot(max_depths, train_results, 'b', label='Train AUC')
line2, = plt.plot(max_depths, test_results, 'r', label='Test AUC')
plt.legend(handler_map={line1: HandlerLine2D(numpoints=2)})
plt.ylabel('AUC score')
plt.xlabel('Tree depth')
plt.savefig("../img/2019-07-29_决策树_1.png")
plt.close()
|

min_samples_split
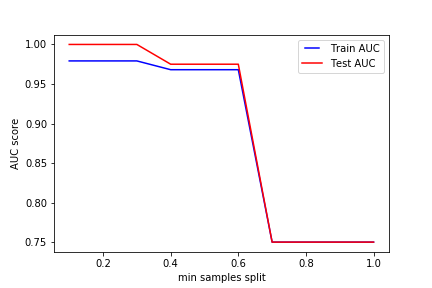
min_samples_split表示拆分内部节点所需的最小样本数。 这可以在考虑每个节点处的至少一个样本,并考虑每个节点处的所有样本之间变化。 当我们增加此参数时,给与树更多的约束,因为它必须在每个节点处考虑更多样本。 在这里,我们将从10%到100%的样本中改变参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| min_samples_splits = np.linspace(0.1, 1.0, 10, endpoint=True)
train_results = []
test_results = []
for min_samples_split in min_samples_splits:
dt = DecisionTreeClassifier(min_samples_split=min_samples_split)
dt.fit(x_train, y_train)
train_pred = dt.predict(x_train)
false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate, thresholds = roc_curve(
y_train, train_pred, pos_label=2)
roc_auc = auc(false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate)
train_results.append(roc_auc)
y_pred = dt.predict(x_test)
false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate, thresholds = roc_curve(
y_test, y_pred, pos_label=2)
roc_auc = auc(false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate)
test_results.append(roc_auc)
from matplotlib.legend_handler import HandlerLine2D
line1, = plt.plot(min_samples_splits, train_results, 'b', label='Train AUC')
line2, = plt.plot(min_samples_splits, test_results, 'r', label='Test AUC')
plt.legend(handler_map={line1: HandlerLine2D(numpoints=2)})
plt.ylabel('AUC score')
plt.xlabel('min samples split')
plt.savefig("../img/2019-07-29_决策树_2.png")
plt.close()
|

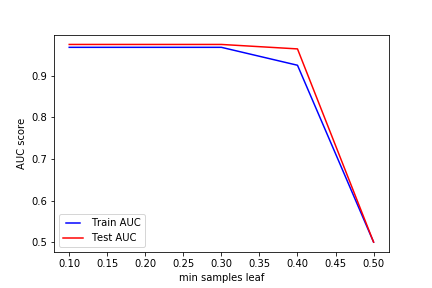
min_samples_leaf
min_samples_leaf是叶节点所需的最小样本数。 此参数类似于min_samples_splits,但是,这描述了叶子(树的基础)处的样本的最小样本数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| min_samples_leafs = np.linspace(0.1, 0.5, 5, endpoint=True)
train_results = []
test_results = []
for min_samples_leaf in min_samples_leafs:
dt = DecisionTreeClassifier(min_samples_leaf=min_samples_leaf)
dt.fit(x_train, y_train)
train_pred = dt.predict(x_train)
false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate, thresholds = roc_curve(
y_train, train_pred, pos_label=2)
roc_auc = auc(false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate)
train_results.append(roc_auc)
y_pred = dt.predict(x_test)
false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate, thresholds = roc_curve(
y_test, y_pred, pos_label=2)
roc_auc = auc(false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate)
test_results.append(roc_auc)
from matplotlib.legend_handler import HandlerLine2D
line1, = plt.plot(min_samples_leafs, train_results, 'b', label='Train AUC')
line2, = plt.plot(min_samples_leafs, test_results, 'r', label='Test AUC')
plt.legend(handler_map={line1: HandlerLine2D(numpoints=2)})
plt.ylabel('AUC score')
plt.xlabel('min samples leaf')
plt.savefig("../img/2019-07-29_决策树_3.png")
plt.close()
|

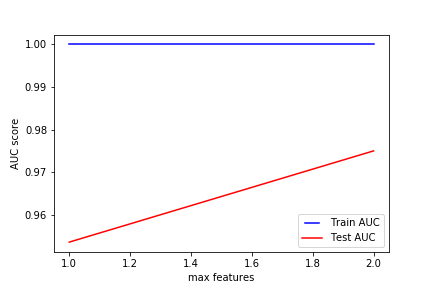
max_features
max_features表示查找最佳拆分时要考虑的要最大特征数量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| max_features = list(range(1, len(iris_target_name)))
train_results = []
test_results = []
for max_feature in max_features:
dt = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_features=max_feature)
dt.fit(x_train, y_train)
train_pred = dt.predict(x_train)
false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate, thresholds = roc_curve(
y_train, train_pred, pos_label=2)
roc_auc = auc(false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate)
train_results.append(roc_auc)
y_pred = dt.predict(x_test)
false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate, thresholds = roc_curve(
y_test, y_pred, pos_label=2)
roc_auc = auc(false_positive_rate, true_positive_rate)
test_results.append(roc_auc)
from matplotlib.legend_handler import HandlerLine2D
line1, = plt.plot(max_features, train_results, 'b', label='Train AUC')
line2, = plt.plot(max_features, test_results, 'r', label='Test AUC')
plt.legend(handler_map={line1: HandlerLine2D(numpoints=2)})
plt.ylabel('AUC score')
plt.xlabel('max features')
plt.savefig("../img/2019-07-29_决策树_4.png")
plt.close()
|

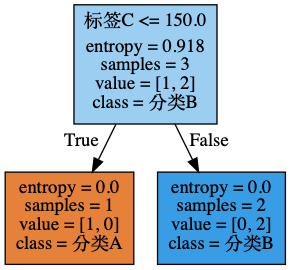
树的可视化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| from IPython.display import display, Image
import graphviz
import pydotplus as pdp
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(clf, out_file = None,
feature_names = ["标签A","标签B","标签C"],
class_names = ["分类A","分类B"],
filled = True,
rotate = False)
graph = pdp.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data)
img = Image(graph.create_png())
|

参考:
- 从机器学习到深度学习:基于Scikit-learn与TensorFlow的高效开发实战
- 决策树(四)决策树调参